numpy.percentile#
- numpy.percentile(a, q, axis=None, out=None, overwrite_input=False, method='linear', keepdims=False, *, weights=None, interpolation=None)[源代码]#
计算指定轴上的数据的 q-th 百分位数.
返回数组元素的 q-th 百分位数.
- 参数:
- a实数的类数组 (array_like)
可以转换为数组的输入数组或对象.
- qfloat 的类数组
要计算的百分比或百分比序列.值必须在 0 到 100 之间(含).
- 轴{int, tuple of int, None}, optional
计算百分位数的轴或多个轴. 默认值是计算沿数组扁平化版本的百分位数.
- outndarray,可选
用于放置结果的可选输出数组.它必须具有与预期输出相同的形状和缓冲区长度,但是如有必要,将强制转换(输出的)类型.
- overwrite_inputbool,可选
如果为 True,则允许通过中间计算修改输入数组 a ,以节省内存. 在这种情况下,此函数完成后输入 a 的内容是未定义的.
- methodstr, optional
此参数指定用于估计百分位数的方法. 有许多不同的方法,其中一些是 NumPy 独有的. 有关说明,请参见注释. 按 H&F 论文 [1] 中总结的 R 类型排序的选项为:
‘inverted_cdf’
‘averaged_inverted_cdf’
‘closest_observation’
‘interpolated_inverted_cdf’
‘hazen’
‘weibull’
‘linear’ (default)
‘median_unbiased’
‘normal_unbiased’
前三种方法是不连续的. NumPy 进一步定义了以下默认"线性"(7.)选项的不连续变体:
‘lower’
‘higher’,
‘midpoint’
‘nearest’
在 1.22.0 版本发生变更: 此参数以前称为"interpolation",仅提供"linear"默认值和最后四个选项.
- keepdimsbool,可选
如果设置为 True,则缩小的轴将保留在结果中,作为大小为 1 的维度. 使用此选项,结果将正确地广播到原始数组 a .
- weights类数组,可选
与 a 中值关联的权重数组. a 中的每个值都根据其关联的权重对百分位数做出贡献.权重数组可以是 1-D(在这种情况下,其长度必须是 a 沿着给定轴的大小)或与 a 的形状相同.如果 weights=None ,则假定 a 中的所有数据都具有等于 1 的权重.只有 method=”inverted_cdf” 支持权重.有关更多详细信息,请参见注释.
在 2.0.0 版本加入.
- interpolationstr, optional
method 关键字参数的已弃用名称.
自 1.22.0 版本弃用.
- 返回:
- percentile标量或 ndarray
如果 q 是一个单独的百分位数且 axis=None ,则结果是一个标量.如果给出了多个百分位数,则结果的第一个轴对应于百分位数.其他轴是在 a 的归约之后保留的轴.如果输入包含整数或小于
float64的浮点数,则输出数据类型为float64.否则,输出数据类型与输入的数据类型相同.如果指定了 out ,则返回该数组.
参见
meanmedian等效于
percentile(..., 50)nanpercentilequantile等效于 percentile,除了 q 的范围在 [0, 1] 中.
注释
numpy.percentile与百分比 q 的行为与参数为q/100的numpy.quantile的行为相同. 有关更多信息,请参见numpy.quantile.参考文献
[1]R. J. Hyndman and Y. Fan, “Sample quantiles in statistical packages,” The American Statistician, 50(4), pp. 361-365, 1996
示例
>>> import numpy as np >>> a = np.array([[10, 7, 4], [3, 2, 1]]) >>> a array([[10, 7, 4], [ 3, 2, 1]]) >>> np.percentile(a, 50) 3.5 >>> np.percentile(a, 50, axis=0) array([6.5, 4.5, 2.5]) >>> np.percentile(a, 50, axis=1) array([7., 2.]) >>> np.percentile(a, 50, axis=1, keepdims=True) array([[7.], [2.]])
>>> m = np.percentile(a, 50, axis=0) >>> out = np.zeros_like(m) >>> np.percentile(a, 50, axis=0, out=out) array([6.5, 4.5, 2.5]) >>> m array([6.5, 4.5, 2.5])
>>> b = a.copy() >>> np.percentile(b, 50, axis=1, overwrite_input=True) array([7., 2.]) >>> assert not np.all(a == b)
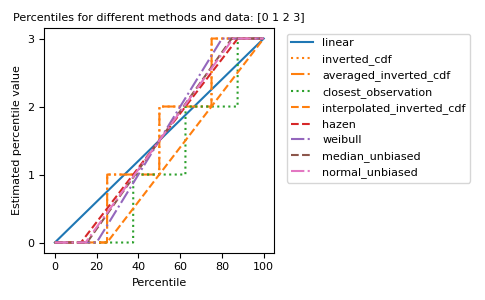
不同的方法可以用图形方式可视化:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt a = np.arange(4) p = np.linspace(0, 100, 6001) ax = plt.gca() lines = [ ('linear', '-', 'C0'), ('inverted_cdf', ':', 'C1'), # Almost the same as `inverted_cdf`: ('averaged_inverted_cdf', '-.', 'C1'), ('closest_observation', ':', 'C2'), ('interpolated_inverted_cdf', '--', 'C1'), ('hazen', '--', 'C3'), ('weibull', '-.', 'C4'), ('median_unbiased', '--', 'C5'), ('normal_unbiased', '-.', 'C6'), ] for method, style, color in lines: ax.plot( p, np.percentile(a, p, method=method), label=method, linestyle=style, color=color) ax.set( title='Percentiles for different methods and data: ' + str(a), xlabel='Percentile', ylabel='Estimated percentile value', yticks=a) ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.03, 1)) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()