numpy.random.RandomState.gamma#
method
- random.RandomState.gamma(shape, scale=1.0, size=None)#
从伽马分布中抽取样本.
样本是从具有指定参数的伽马分布中抽取的, shape (有时指定为"k")和 scale (有时指定为"theta"),其中两个参数都 > 0.
- 参数:
- shapefloat 或 float 的类数组
伽马分布的形状.必须是非负的.
- scale浮点数或浮点数数组,可选
伽马分布的尺度.必须是非负的.默认为 1.
- sizeint 或 int 元组,可选
输出形状.如果给定的形状是,例如,
(m, n, k),那么将抽取m * n * k个样本.如果 size 是None(默认值),如果shape和scale都是标量,则返回单个值.否则,将抽取np.broadcast(shape, scale).size个样本.
- 返回:
- outndarray 或标量
从参数化的伽马分布中抽取样本.
参见
scipy.stats.gamma概率密度函数,分布或累积密度函数等.
random.Generator.gamma新代码应该使用它.
注释
伽马分布的概率密度为
\[p(x) = x^{k-1}\frac{e^{-x/\theta}}{\theta^k\Gamma(k)},\]其中 \(k\) 是形状, \(\theta\) 是尺度, \(\Gamma\) 是伽马函数.
伽马分布通常用于对电子元件的故障时间进行建模,并且自然地出现在泊松分布事件之间的等待时间相关的过程中.
参考文献
[1]Weisstein, Eric W. “伽马分布.” 来自 MathWorld–一个 Wolfram 网络资源. https://mathworld.wolfram.com/GammaDistribution.html
[2]维基百科,"伽马分布",https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_distribution
示例
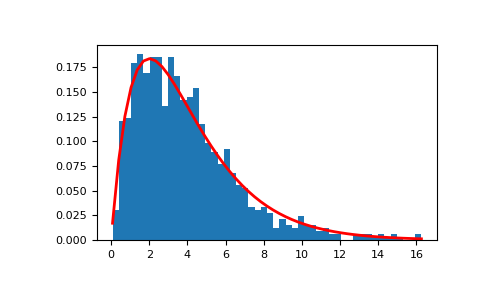
从分布中抽取样本:
>>> shape, scale = 2., 2. # mean=4, std=2*sqrt(2) >>> s = np.random.gamma(shape, scale, 1000)
显示样本的直方图,以及概率密度函数:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import scipy.special as sps >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s, 50, density=True) >>> y = bins**(shape-1)*(np.exp(-bins/scale) / ... (sps.gamma(shape)*scale**shape)) >>> plt.plot(bins, y, linewidth=2, color='r') >>> plt.show()